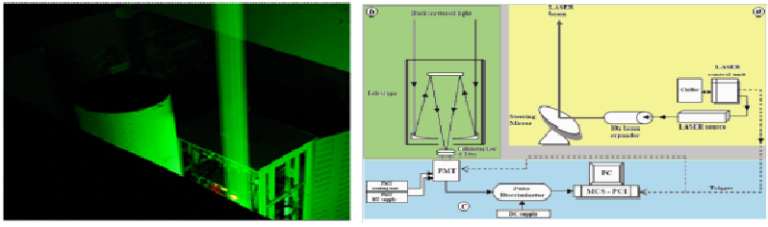
Mie Lidar
A Mie Lidar was developed at ARIES using optimized optics, mechanics and advanced electronics for data acquisition and processing. Optical design Design analysis for 380 mm Cassegrain telescope and black end detection optics were carried out in ZEMAX-EE simulation package to optimize system parameters. A high power Q-switched, Nd: YAG solid state pulsed laser form Quanta systems S.P.A, Italy was used as transmitter for the LIDAR system. The Detector and Data Acquisition System (DDAS) of LIDAR comprises of detection unit containing Photo multiplier tube (PMT) as detector with cooling unit and power supply unit. It also includes amplifier and discriminator unit along with Multi-Channel Scalar (MCS) package. A computational program was developed implementing Fernald method to compute extinction coefficients and aerosols optical depth in the Matrix Laboratory (MATLAB) environment. A motorized roll-off-roof was designed and installed for carrying out Lidar observations at night. The system is presently employed for study of atmospheric aerosols and clouds via the Mie scattering up ~ 20Km above ground level during night time. Systematic error on retrieved extinction profiles by taking fixed Lidar ratio of 30 over the entire range for our observations showed the variation is about 10-12% in the lower altitudes and 5 -7 % in the higher altitudes. Mie Lidar system was employed to observe thin and thick cloud during January 2010. Thin cloud layer was observed at about 10 km and thick cloud layer was seen between 5 and 9 km. Results are also compared with MODIS & AERONET and agree within one standard deviation.